Introduction
Managing timesheets manually can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Automating the process of extracting data from timesheet PDFs and storing it in Google Sheets can save time and improve efficiency. In this blog, we'll walk through how to set up an automation using n8n, an open-source workflow automation tool, to extract data from a timesheet PDF and store it in a Google Sheet.
Business Challenge
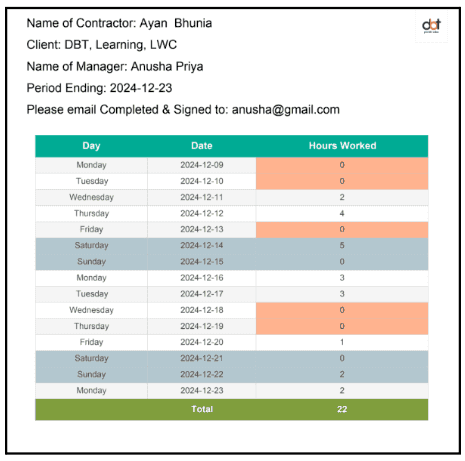
Organizations often receive timesheets in PDF format, making it difficult to extract and analyze data efficiently. Manually copying data into spreadsheets is not only tedious but also prone to human error. An automated solution is required to:
Extract structured timesheet data from PDFs.
Store and organize the extracted data in Google Sheets.
Minimize manual effort and reduce errors.
Improve data accessibility for payroll and reporting purposes.
Requirement
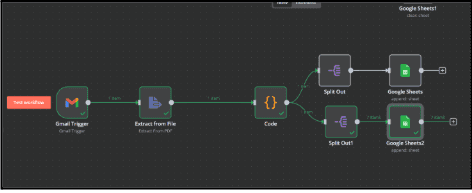
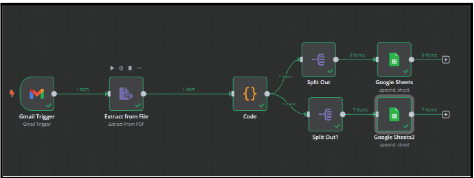
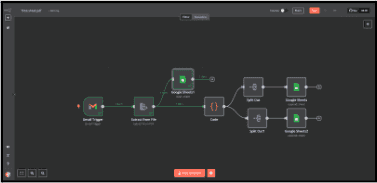
The workflow should automatically detect new timesheet PDFs using n8n, extract relevant data, format and structure the extracted information for better readability, and store the processed data in Google Sheets. With this automation, businesses can eliminate manual efforts, reduce errors, and speed up payroll processing while ensuring accurate timesheet tracking.
Steps to achieve the Requirement
- Set up n8n
- Set up Gmail trigger to detect new timesheet PDFs
- Extract data from the timesheet PDF
- Process and format the extracted Data
- Split data into different categories
- Store processed data in google sheets
- Automate and test the workflow
1. Setting Up n8n for Automation
1.1. Install and Access n8n: You can use n8n in different ways.
**Self-hosted:** Install on your local machine or server.
**Cloud version**: Sign up for n8n Cloud to get started quickly.For self-hosting, install using npm: https://docs.n8n.io/hosting/installation/npm/
1.2. To Enable Gmail API Access.
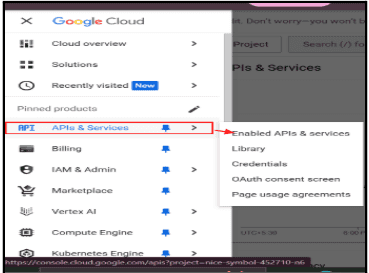
1.2.1. Go to Google Cloud Console.
1.2.2. Sign in with your Google Account.
1.2.3. In the top navigation bar, select an existing project or Create a new
project .
1.2.4. Click APIs & Services to proceed.
1.2.5. In the left side menu Go to APIs & Services > library.
1.2.6. Search for Gmail API in the search bar.
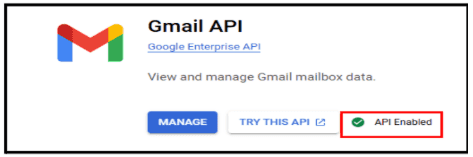
1.2.7. Click on Gmail API in the search bar.
1.2.8. Click Enable to activate it.
1.3. To Get Gmail Credential
1.3.1. In the left side menu Go to APIs & Services >Credentials.
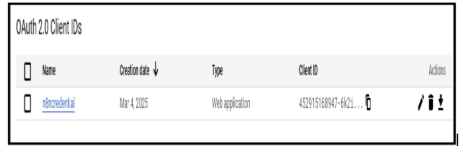
1.3.2. Click Create Credentials and select OAuth 2.0 Client ID.
1.3.3. Get Client ID & Secret and connect it to n8n.
2. Set up Gmail trigger to detect new timesheet PDFs
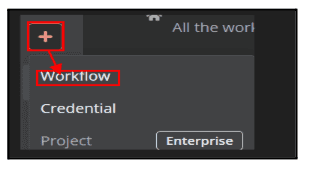
2.1. Click ‘+’ symbol And select workflow
2.2. Click ‘+’ symbol
2.2.1. In the search box, type 'Gmail' and select the 'On Message Received' node.
2.2.2. Select "On Message Received" under the Gmail node.
2.3. Configure Gmail Trigger Node
Once you have added the Gmail Trigger node, you need to configure it.
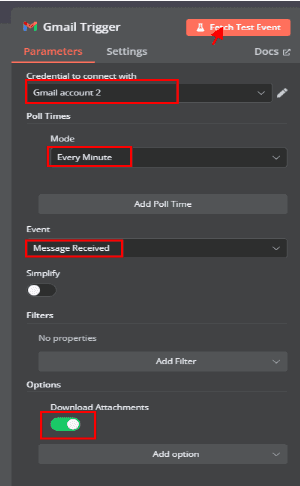
2.3.1. Credential Selection
Choose the Gmail account that you want to connect to n8n.If no credentials exist, you must authenticate with your Goggle account.
2.3.2. Poll Times
In this example, the mode is set to "Every Minute", meaning n8n will poll for new emails every 60 seconds.
2.3.3. Event Selection
Set the event type to "Message Received", which means the workflow will trigger when a new email arrives.
2.3.4. Filters (Optional)
You can add filters to only trigger the workflow for specific emails.
Example filters: From a specific sender, Subject contains a keyword, etc.
2.3.5. Options
Download Attachments: Enabled ✅ (This ensures that any attachments in the email are fetched for further processing).
2.4. Test the Trigger
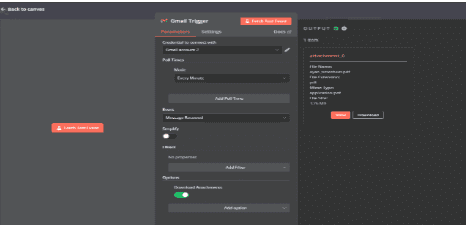
2.4.1. Click "Fetch Test Event" to check if the node is working properly. If everything is set up correctly, you will see email data in the output.
2.4.2. Click Back to canvas.
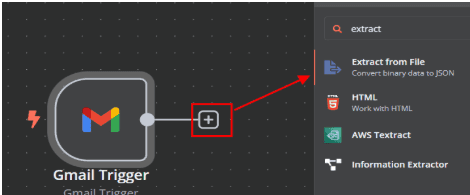
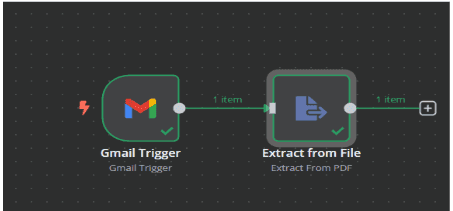
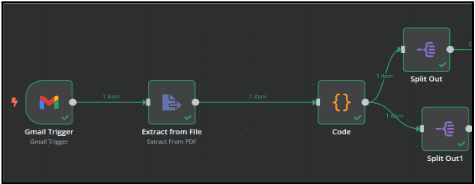
3. Extract data from the timesheet PDF
3.1. After clicking the "+" symbol at the end of the Gmail Trigger node, you can
add the next node in your workflow.
3.2. In the search box, type "Extract from File" and select the
"Extract From PDF" node.
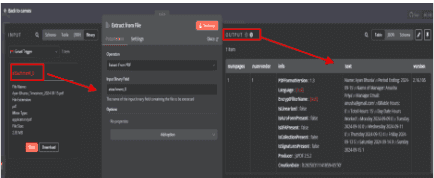
3.3. Input Section (Left Side)
The "Gmail Trigger" node successfully fetched an email with an attached PDF file.
3.4. Extract from File Node (Right Side)
3.4.1. Operation: Select "Extract From PDF" , This ensures the node
extracts text from the PDF file.
3.4.2. Input Binary Field: Give the name is “attachment_0”.
3.4.3. The binary field that contains the PDF file.
3.5. Click "Test step" to check if the extraction is successful.
3.5.1. If successful, the extracted text will appear in the Output section.
3.6. Click Back to canvas.
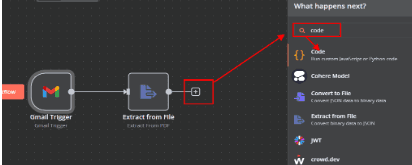
4. Process and format the extracted Data
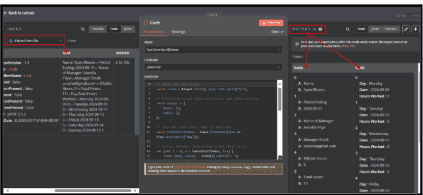
4.1. Click ‘+’ symbol, In the search box, type 'Code' and select the ‘code node’.
4.2. In the Code node, set the language to JavaScript.
4.3. Write a script to process and structure the extracted text.
4.4. Execute the node to convert extracted text into basic and Table fields.
4.5. Check the Output panel for structured data.
// Split text into lines
const lines = $input.first().json.text.split("\n");
// Initialize result object with basic and table sections
const result = {
basic: \[],
table: \[]
};
// Find the index where "Day" is mentioned
const tableStartIndex = lines.findIndex(line => line.startsWith("Day"));
// Extract metadata (everything before "Day" line)
for (let i = 0; i < tableStartIndex; i++) {
const \[key, value] = lines\[i].split(": ");
result.basic.push({
A:key,
B:value
});
}
// Process table data (everything after "Day" line)
for (let i = tableStartIndex + 1; i < lines.length - 1; i++) {
const parts = lines\[i].split(" ");
if (parts.length === 3) {
const row = {
"Day": parts\[0],
"Date": parts\[1],
"Hours Worked": parts\[2]
};
result.table.push(row);
}
}
// Add the total row
const totalParts = lines\[lines.length - 1].split(" ");
result.table.push({
"Day": "",
"Date": "Total",
"Hours Worked": totalParts\[1]
});
// Return the output in JSON format
return \[{ json: result }];5. Split data Into Different Categories
5.1. Click the Dot,
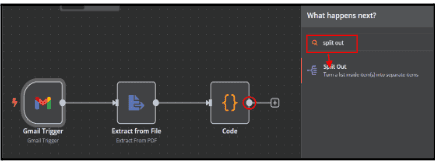
5.1.1. In the search box, type 'Split out' and select it.
5.1.2. Set up the nodes to Separate the data into basic and table formats.
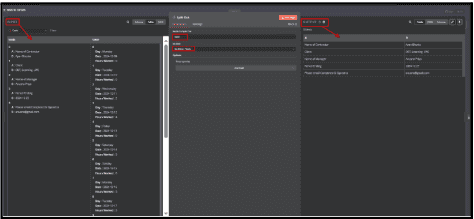
5.2. To Split the basic data
5.2.1. Connect the Code node to the Split Out node.
5.2.2. In the Split Out node, Type ‘basic’ in Field to split out.
5.2.3. Choose the option to include No other fields .
5.2.4. Click Test step.
5.2.5. Verify the structured output in the Output section.
5.3. To split the table data, Repeat the steps 5.1 & 5.1.1 & 5.1.2.
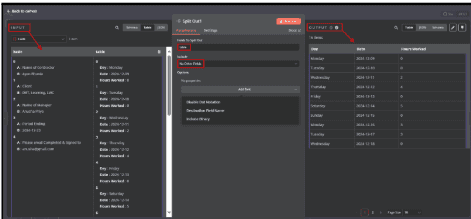
5.3.1. Connect the Code node to the Split Out node 1.
5.3.2. In the Split Out node 1, Type Table in Field to Split Out .
5.3.3. Choose whether to include or remove additional fields in the output.
5.3.4. Click the Test step.
5.3.5. Verify the structured output in the Output section.
5.4. Click Back to canvas.
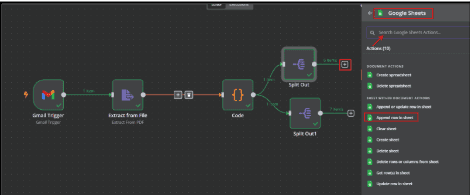
6. Store processed data into google sheets
6.1. To Connect Google Sheets nodes
6.1.1. Click the ‘+’ symbol to search for Google Sheets, and select it.
6.1.2. Select the sheet within Document Actions and set it to Append Row in
Sheet.
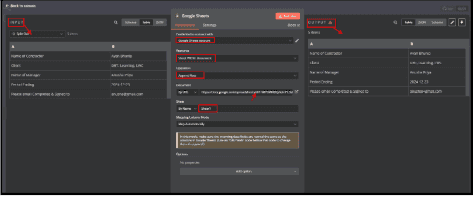
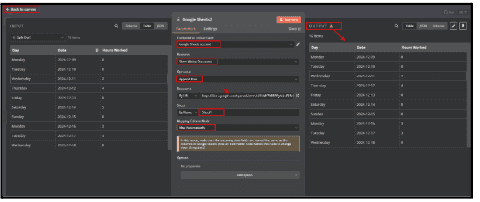
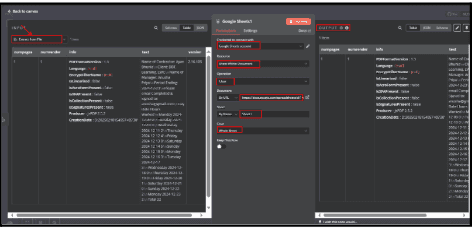
6.2. Under "Credential to connect with", select Google Sheets account.
6.2.1. If not connected, click "Edit" (pencil icon) and authorize access to your Google Sheets.
6.3. Select "Sheet Within Document" in the Resource dropdown.
6.3.1. This means the node will interact with a specific sheet inside a spreadsheet.
6.4. Choose "Append Row" in the Operation field.
6.4.1. This operation will add new rows at the bottom of the sheet.
6.5. Under Document, choose "By URL".
6.5.1. Paste the Google Sheets URL into the provided field.
6.5.2. This links the node to your specific Google Sheet.
6.6. Under Sheet, select "By Name" and enter the sheet name (Sheet1 in this case).
6.6.1. Ensure this matches the exact name of the sheet inside your Google
Sheets document.
6.7 In Mapping Column Mode, choose "Map Automatically".
6.7.1. This ensures that n8n maps incoming data fields to the corresponding
columns in Google Sheets.
6.8. Click "Test Step". If successful, data should appear as a new row in your Google Sheet.
6.8.1. Click Back to canvas.
6.9. To get the Basic Output in Google sheet
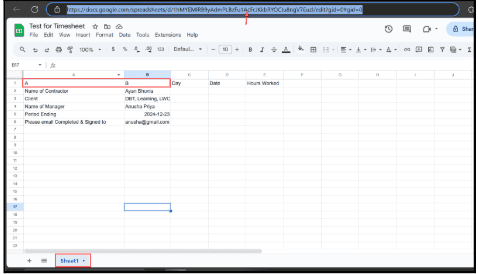
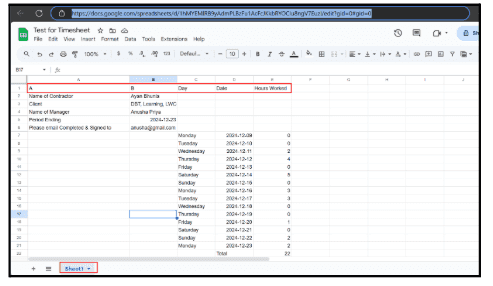
6.9.1. Open Google Sheets, Create a new spreadsheet, and copy its URL.
6.9.2. Ensure the sheet has appropriate column headers for data storage
6.9.3. Connect the Google Sheets node in your workflow and paste the URL.
6.9.4. Select the correct sheet, such as Sheet1, and map data fields to columns.
6.9.5. Run the workflow to verify the data is correctly added as the basic
Output.
6.10. To get the table Output in Google sheet.
6.10.1. Repeat Steps From 6.1. To 6.6.
6.11. In Mapping Column Mode, choose "Map Automatically".
6.12. Click "Test Step".
6.12.1. Click Back to canvas.
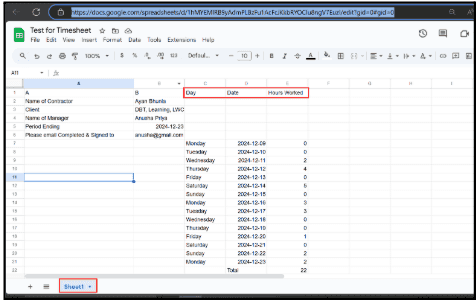
6.12.2. The table data will be saved in the specific Google Sheet.
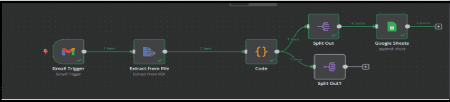
7. Automate and test the workflow.
7.1. To Execute the workflow.
7.1.1. Enable the Gmail Trigger to automate email retrieval.
7.1.2. Ensure all nodes are properly connected and configured.
7.1.3. Click Test Workflow to test the automation.
7.1.4. Check Google Sheets to confirm data is stored correctly.
8. To Ensuring the data accuracy in Automated workflows
8.1. Extract data from the PDF using the Extract from File node.
8.2. Configure the Google Sheets1 to clear the existing data before storing new
data.
8.3. Click Test Workflow or enable scheduling to automate the process.
8.4. Select Google Sheets1 and set operation to Clear to remove previous
data.
8.5. Select By URL and paste the Google Sheets link.
8.6. Select Sheet1 to store the extracted data and set Clear to Whole Sheet.
8.6.1. Click Back to canvas.
8.7. Open Google Sheets and locate the specified sheet.
8.7.1. Confirm that the sheet is empty, ensuring all previous data has been removed.
8.7.2. Removes old data to keep new records accurate.
8.7.3. Maintains accuracy and prevents duplication in timesheet records.
Leave a Comment